Description: I’m currently taking a specialization on Coursera for SEO. It’s made up of 6 total courses. I’m going to take notes on each class here. I’ve provided the link below if you’re interested in learning or getting a specialization certificate from Coursera.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Course 1: Introduction to Search Engine Optimization
- Week 1 – Didn’t take notes
- Week 2 – Didn’t take notes
- Week 3 – SEO Best Practices
- Create high-quality content
- Create a home page that helps search engines understand what your site is about
- Outside links increase authority on your site
- Clear hierarchy – Navigating your website should be intuitive and easy to find
- Three Major types of ranking factors
- On-Page Factors
- Off-Site Factors
- Domain Factors
- Resources:
- Poor SEO practices
- Use of the same text repeatedly in the backlink profile (Backlink – an incoming hyperlink from one web page to another website)
- Keyword stuff – Repeating the same keyword in the page title and on-page copy
- Invisible keyword text – Hidden to users but visible to search engines.
- Meta-keyword tag overload – Loaded up meta keywords tag in the site’s HTML with spammy keywords
- Updates to Algorithms to keep in mind
- Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) – The algo looks for commonly related words to the KEYWORDS to determine what the article is about. For example, if the keyword is baseball, other words the algo looks for is a bat, pitcher, dugout, home run. Anything that’s associated with baseball. The algo then knows it’s really about baseball.
- Inbound links & link neighborhoods – The more sites that are of the same category (i.e. sports) that link to your site and the more that you link to “neighborhood” categories (i.e. sports) the higher your ranking goes. Also the links you link to matters as well. If a site is spammy then it reduces your ranking.
- *(My own thoughts – Embed a viral feature in your product. i.e. Youtube allowing you to embed their video into your website)
- Larger brands have an easier time reaching higher rankings because many times they have partners, vendors, and customers forced to link back to their website.
- Thin/ Low-Quality Sites – Few pages with useful content
- Largely similar content
- No content
- Content scraped from other sites (Whoever posted first gets ranked better)
- Duplicated pages
- An excessive amount of ads
- Poor Navigation
- Auto-generated content (Program generated with keywords but gibberish)
- Squeeze Pages (Landing page everything on one page)
- Doorway Pages (Built for search engine)
- Meta Refresh (Go to a page and it will change to another page before you leave)
- Bad Guest posts – Create low-quality posts
- If your content is not beneficial for a customer or relevant then get rid of it.
- Resources:
- Links from authoritative sites are good.
- Negative impact to rank is manipulative link practices:
- Link network – Creating a lot websites and linking to each other
- Links in comments by bots
- Paid links. These are harder to track but Google will look for where the link is. If it’s on the side bar or if it says sponsored content.
- Irrelevant links. Links from sites that have nothing to do with your business.
- Mobile friendly sites are ranked higher when searching on mobile
- Resources:
- How to work with penalties:
- If you have high similarity on content remove duplication
- Create original unique content for key pages
- Check analytics data to see if you see any odd drops in search results
- Google Search Console – Sometimes Google will tell you why you got a penalty
- Review Google blogs to see if they have any updates
- Check MozCast
- Check other social media channels to see if anyone has the same issues
- Verify your backlink health
- You might be manually assessed a penalty. If that happens you need to correct the issue and ask for a reconsideration request to googles team.
- Resources:
- Topic Association
- The site contains key terms as well as relevant additional terms that relate to each other contextually
- Search engines analyze contextual meaning to find relevance to topic/theme
- Don’t just use one keyword. Use words that are also associated with the primary keyword you want to use.
- I.e. Winemaking – Wine, Vineyard, Wine Growing, Wine Production
- i.e. Certification – Course, class, lecture, program, certificate
- Use synonyms of your keyword
- Use relevant keywords support your chosen keyword or topic of your page
- Long tail keywords – longer words or phrases
- Resources:
- Semantic Relationship
- Semantically related key words
- Relevancy and semantic relationships
- Semantic analysis looks at how words are related
- Site about baseball – Pitcher, bat, run
- Resources:
- Brand recognition increasing SEO
- Important marketing strategy and boosts SEO efforts
- Big Brands usually have a strong social media presence with lots of customers interaction
- They have contact information – Address, phone number, email, contact form
- Established history (domain name history)
- More mentions around the web and social media
- Google Adwords
- When you create naturally buzzworthy service, people will start mentioning you more, linking to your site, etc.
- Customer service can actually play into your SEO efforts
- Create great content
- Develop social presence
- Acquire links
- Helps cultivate branded search
- Resources:
Course 2: Search Engine Optimization Fundamentals
- Week 1 – Getting Started and Introduction to On-page SEO
- Key elements of effective SEO Strategy
- How to select keywords and perform keyword research
- Relevancy, intent, and competitiveness
- Analyze keyword competitiveness
- Consumer psychology and search behavior
- On-page SEO analysis to identify opportunities to improve a website’s search optimization
- Key areas of SEO:
- On-site optimization – Optimizing elements of a page or groups of pages to optimize for SEO
- It’s called on-page optimization because it’s elements or code of a page which involves:
- Content
- Keyword Choice
- Meta Data
- It’s called on-page optimization because it’s elements or code of a page which involves:
- Technical Optimization – How well a site is seen and understood by search engines.
- Improve code of the site and structure of it
- You can make great on page changes but if search engines can’t find it it’s useless
- Off-site optimization – Actions you can take outside of your website to optimize your website
- Similar to public relationships
- Creating relationships with other webmasters
- Acquiring inbound links
- Engaging in social media
- Writing link worthy content
- On-site optimization – Optimizing elements of a page or groups of pages to optimize for SEO
- How to select keywords and perform keyword research
- Resources:
- On-site Optimization
- Core concepts
- Meta Data and Meta Tag
- Recognize individual Meta-Data elements from a search result
- Anatomy of a search results
- Meta Data – When you search for something and you get summary information of the site (Data that describes other data)
- Title (Title Tag)
- Site URL (Website address)
- Site description (Meta Description)
- Meta Tags – are used when you code a website to help identify important information about the page (Found in source code)
- Meta Data – When you search for something and you get summary information of the site (Data that describes other data)
- Title Tags
- View source to see code
- <Title></Title> tag
- Use Moz bar to find page elements
- One of the most important on-page elements to optimize
- Recommendation order of Title tag <title> Description of page | Brand</title>
- Google places more emphasis on the beginning of the title tag rather than the end. Put keywords closer to the beginning of title tag.
- Title tags no longer than 55-60 characters in length. 55 or less is better.
- Use only most important keys (Use two keywords in title tag)
- Avoid special characters
- Shorten brand name if it’s too long
- Meta Descriptions
- Meta descriptions don’t help pages rank BUT it can help direct website traffic
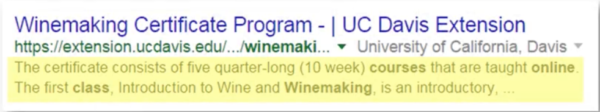
- Metadata is highlighted in yellow
- Describes what the page is about
- To see the metadata you need to –> Look at source code –> right click –> view page source –> “meta name = description”
- You can also use the Moz bar add-on.
- Search engines will not look for keywords in meta description BUT it helps get people to click on your site.
- Keywords are bolded in the search engine helping people click the site
- About 1-2 sentences (160 characters in length) show on the description.
- Description of content, having keywords, and CALL TO ACTION (CTA) telling a client what to do they are more likely to listen and follow the direction.
- Another good reason to have good meta description about your page is social media posts. When someone shares your article, the description will be shown on the shared thread.
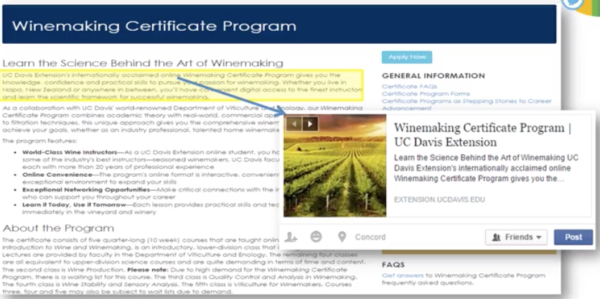
- It needs to be catchy to get people to click
- Best practices:
- 160 characters or less
- Include keywords
- Include CTA
- Meta Keywords Tag
- Not a focus of SEO anymore
- Search engines weren’t capable of understanding a site so Meta Keywords Tag was necessary
- Not seen by users
- Some search engines use it but it’s very rarely the case (Baidu still uses it – Must be in chinese)
- Death of Meta keywords
- URL Optimization
- Optimize through Keywords, subdirectories, parameters
- URL definition – Address that loads a particular site
- URL should have keywords in it towards the beginning
- Not as important but still useful.
- Keywords help for Off-page SEO when people are linking to your site. It helps viewers determine how relevant it is.
- Keywords should be used in subfolders/subdirectories
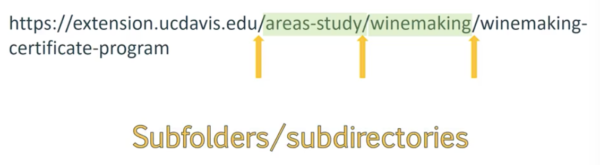
- Keywords in URL will show up in bold
- Parameters in green below

- Being part of the website creation and URL naming as an SEO expert is best but often not the case. You can change it later on but it erases the credibility the name of the site already created. It’s like getting a new credit score. You lose your past history.
- URL Best Practices
- don’t change URLs lightly
- Use 301 redirects if you do
- Optimize URL from the start
- Use keywords in URL
- Use keywords in subdirectories
- Keep URLs short
- Heading Tags
- Primary heading H1 – Most important
- Secondary heading H2 – Important
- H3 and on aren’t really used for search engines for ranking
- Optimize headings with keywords if they are naturally incorporated.
- View source code or Moz add-on to view heading tags.
- Sometimes heading tags are used when they shouldn’t be used. This should be optimized.
- Use keywords in heading tags as much as possible if you can make it seem natural.
- Content and Optimizing Unique Content
- Make keywords fit naturally
- Make content relevant to the theme of your site
- Well organized in subdirectories
- Create your own unique content
- Copied content does not help rank
- If you use other peoples content it could hurt you
- Link back to the page you are quoting
- Google gives credit to the first person who created the content
- Don’t duplicate your content. Each page should be unique
- Copying and changing words does not make it unique
- Duplicated pages will cannibalize the other
- Add video or images
- Adding video, images, links, and downloads makes your content better because it’s usually more useful to a viewer.
- If it’s just a block of text, Google doesn’t think it’s as helpful.
- When you link to another site make sure they aren’t spammy sites
- Use keywords but not too many of them. If you do, Google can view it as SPAM.
- It should sound natural
- Use synonyms. Google can view synonyms and reinforce the theme of your keywords and article.
- Linking
- Link to other relevant pages on the site
- Helps search engines to crawl your site
- Link with anchor texts (Don’t link with “click here” but rather link the keywords to the other page about the keyword)
- Best practices:
- Relevant, well-organized, and unique
- Do no “over-optimize”
- Use synonyms for your keywords to help search engines understand your page
- Use writing at the level of your intended audience. It helps with user-friendliness
- Add resources: Images, documents, Video, and relevant links
- Analyzing a Website Using a Web Crawler
- You can analyze a website all at once using a web crawler
- Export data to Excel
- Resource:
- Crawler or Spider – Screaming Frog
- Core concepts
- Key elements of effective SEO Strategy
- Week 2 – Introduction to Off-site/page SEO
- We’ll learn:
- Link analysis
- Create and edit backlink
- Use social media to build brand authority
- Off-site SEO are the efforts that you can take to optimize your website off your site.
- Building links to your site
- Build brand awareness on social media
- Differentiate from high PageRank to earning site authority
- PageRank -Algorithm
- Created by Larry Page
- It was an algorithm that analyzed web links to determine the relative importance of websites
- The term isn’t used as much
- When another website links to your website, it’s counted as a vote
- The more links the higher the page rank (0-10)
- All websites started at 0
- Twitter was a 10
- 2013 was last time PageRank was updated. No longer used
- Ranking factors are unknown but links are important. Too many people manipulated the linking technique.
- Linking to high-quality websites matters more now.
- How Google Analyzes links
- Amount of links your website has
- Quality of the links
- The relevance of the links to your site (Are they connected in a theme?)
- Placement of the links
- Footer and sidebar are less valuable, possibly spammy.
- Partner or Sponsor text is not good.
- The best type of link is surrounded by text, so within the body of the text.
- Click here anchor texts aren’t good. They should be key words that are the text that is used as a link.
- Google also looks if you’re doing reciprocal links. If you are, they both become invalid.
- Link disavow tool – Webmasters can disavow bad links with the Google Disavow Tool
- Try removing links yourself before using these tools
- Acquire new backlinks from authoritative sites
- Create strong backlinks – Moz
- Social media strategy to enhance SEO
- Twitter and Pinterest for SEO
- Google has stated they do not factor in social media for ranking but Google looks at links. Links and tweets don’t directly impact your SEO but it can increase visibility in search results
- By getting more brand awareness, this does help increase your ranking.
- Pinterest boards are indexed on search engines
- Rank well for long tail keywords
- Boards with active followers rank better
- Social media has secondary benefits
- Resources:
- We’ll learn:
- Week 3 – Introduction to On-site Optimization (Technical SEO)
- What we’ll learn:
- Building a strong structural foundation for your site for search engine robots to search and index
- HTML and XML sitemaps and robots.txt
- Learn about common error codes – temporary or permanent redirects can help user experience and preserve authority of your site
- Technical SEO focuses on how well search engines can crawl your site and index your content
- Order of operations for an optimized SEO strategy:
- Technical SEO
- On-page/site SEO – Content/Keywords
- Off-page SEO signals
- Technical SEO concerns:
- XML sitemaps
- Robots.txt files
- Site errors
- 404 page best practices
- Appropriate redirects
- HTML sitemaps vs. XML sitemaps – Need both for your website design
- Sitemaps point search engines to pages on your site. They help make sure pages are not missed by crawlers
- HTML sitemaps are easy to read and understand by users
- XML sitemaps are made for search engines
- Includes unique information about each URL
- When the page was last updated
- How often pages change
- Page importance in relation to other pages on your site
- XML sitemaps are especially helpful for new sites
- Websites are found by crawlers using site links so it takes some time before new sites are found.
- You can upload your sitemap to Google or Bing which helps inform search engines about your new website and pages
- You can create an XML sitemap for your website with Screaming Frog tool
- Includes unique information about each URL
- Robots.txt – Protocol to specify which pages to NOT index
- Simple text file uploaded to the server
- Crawlers will first go to your websites robots.txt file to see if there are any instructions on what pages not to crawl.
- Robots can choose to ignore info in this file. Search engines and known brands tend to respect this file
- Some bots are used to scan for vulnerabilities in order to hack a site
- Others harvest emails
- Your robots file is a public file so anyone can see what pages you don’t want crawlers to see.
- Robots.txt file
- robots.txt files are found on a websites main url like coursera.org/robots.txt
- The top portion of the file basically is a description to describe the file. It’s not necessary but most CMS websites automatically include it.

- Must be used at the root of your host:
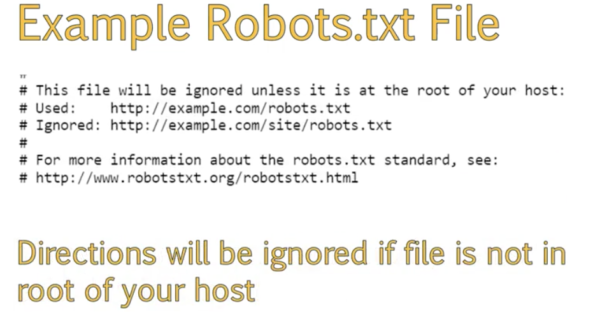
- Next section describes what user-agent aka what crawlers should follow the disallow crawling. You could specify Google or Bing not to crawl these pages but the asterisk is a catch-all for all robots should not crawl your site.

- Crawl-delay determines how many seconds before a crawler can access another page to your site so it doesn’t crash your site.
- Pound or hashtag is used for notes for humans to read. Crawlers overlook them.
- Overcoming Error Codes
- Frustrating for user and causes issues for SEO.
- HTTP response status codes – Helps developers determine what went wrong with a site that couldn’t load.
- 3 digit codes
- They either start with 4XX or 5XX
- Common status codes
- 200 – Page loaded properly
- 404 – Page cannot be found
- Not to include in the index
- Soft 404s are pages that no longer exist but show they are loading okay as 200.
- This happens when content is removed but the page is left in place
- This usually happens on e-commerce sites when a product is no longer being sold or on real estate sides where the listing is no longer available.
- Very bad for SEO
- SEO will consider the page existing but containing the same error message which looks like duplicate content or thin content/not helpful.
- You can use google search console to see which sites are possibly loading as soft 404 pages.
- 500 – Server error
- Temporary and usually gets corrected
- Developer might need to look at server logs to determine issue if they are not temporary
- 503 – Service unavailable
- You’ll see it when the server is down for maintenance
- Redirects 101
- Three types of redirects
- Permanent
- Temporary
- Meta refresh
- A redirect is a status code
- Common redirect codes applicable to SEO
- 301 HTTP status code – Permanent
- Search engines will give the same ranking to the new page as the old
- Usually about 5% of page authority is lost
- 302 HTTP status code – Temporary
- Search engines will not give the same ranking to the new page as the old
- Generally, recommend 301 over a 302 site redirect
- Chain redirecting (A –> B –> C) should have A –> C and B –> so you can retain more of your site authority.
- Redirects for pages that no longer exist, don’t automatically redirect to the home page. Redirect to a specific page, if not then category level page, and finally home page if you need to. This helps search engines with navigating the website and a better user experience.
- 307 HTTP status code – Newer on for 302 but you’ll still see 302
- 301 HTTP status code – Permanent
- Meta refresh status code
- Executed at the page level instead of the server itself
- Slower
- “If you are not redirected within five seconds” — Meta refresh
- Poor user experience
- Doesn’t tell search engines what to do
- Three types of redirects
- Best practices for 404 pages
- Error page when page is not found
- Most common error pages
- Search engines know how to handle 404 sites so it doesn’t impact it as much but you should still remove as much 404 pages as possible.
- Soft 404 pages are more problematic. They should be fixed.
- Sometimes 404 pages are just what you need.
- 404 pages that have significant authority should be redirected to preserve authority. Send to a relevant page or category, and lastly home page.
- On the 404 page, a best practice is giving them helpful links to other relevant pages on your site.
- Helps with crawlers too because it helps the crawler crawl the rest of your site
- Display Error message with a description so they know what happened
- Include a call to action to know what to do next
- Home page link
- Search box to search for other things on the website.
- Tools:
- Resources:
- Technical SEO by Hubspot
- The Art of SEO: Mastering Search Engine Optimization
- What we’ll learn:
- Weed 4 – Keyword Theory & Research
Pingback: Chiang Mai – Day 15 – MilliardCo.
Pingback: Chiang Mai – Day 18 – MilliardCo.